Abstract
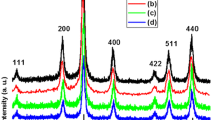
We synthesized by electrostatic self-assembly route in basic solution Fe3O4–cysteine/RGO and Fe3O4/RGO–cysteine nanocomposites. In this method, electrostatic interaction was created via negatively charged surface of the reduced graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide–cysteine sheets and positively charged surface of the Fe3O4 and Fe3O4–Cys nanoparticles in aqueous solution. The structural and magnetic properties of the prepared samples were analyzed by x-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Raman spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM), respectively. The dependences of magnetization as a function of applied field using a vibrating sample magnetometer exhibit S-like curves, indicating a magnetic hysteresis behavior for all samples. It clearly showed that, the nanocomposites showed a reduction of saturation magnetization to the Fe3O4 nanoparticles.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gong, J.L., Wang, B., Zeng, G.M., Yang, C.P., Niu, C.G., Niu, Q.Y., Zhou, W.J., Liang, Y.: Removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution using magnetic multi-wall carbon nanotube nanocomposite as adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 164, 1517–1522 (2009)
Chen, L., Xu, Z., Dai, H., Zhang, S.: Facile synthesis and magnetic properties of monodisperse Fe3O4/silica nanocomposite microspheres with embedded structures via a direct solution-based route. J. Alloys Compd. 497, 221–227 (2010)
Kaminski, M.D., Nuñez, L.: Extractant-coated magnetic particles for cobalt and nickel recovery from acidic solution. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 194, 31–36 (1999)
Chen, C., Hu, J., Shao, D., Li, J., Wang, X.: Adsorption behavior of multiwall carbon nanotube/iron oxide magnetic composites for ni(II) and sr(II). J. Hazard. Mater. 164, 923–928 (2009)
Chang, Q., Deng, K., Zhu, L., Jiang, G., Yu, C., Tang, H.: Determination of hydrogen peroxide with the aid of peroxidase-like Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as the catalyst. Microchim. Acta 265(165), 299–305 (2009)
Cheng, Y., Liu, Y., Huang, J., Li, K., Xian, Y., Zhang, W., Jin, L.: Amperometric tyrosinase biosensor based on Fe3O4 nanoparticles-coated carbon nanotubes nanocomposite for rapid detection of coliforms. Electrochim. Acta 54, 2588–2594 (2009)
Gao, G., Wu, H., Zhang, Y., Wang, K., Huang, P., Zhang, X., Guo, S., Cui, D.: One-step synthesis of Fe3O4@C nanotubes for the immobilization of adriamycin. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 12224–12227 (2011)
Wu, D.Q., Zhang, F., Liang, H.W., Feng, X.L.: Nanocomposites and macroscopic materials: assembly of chemically modified graphene sheets. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 6160–6177 (2012)
Ren, J.G., Wu, Q.H., Tang, H., Hong, G., Zhang, W., Lee, S.T.: Germanium–graphene composite anode for high-energy lithium batteries with long cycle life. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 1821–1826 (2013)
Ren, J.G., Wu, Q.H., Hong, G., Zhang, W.J., Wu, H., Amine, K., Yang, J., Lee, S.T.: Silicon–graphene composite anodes for high-energy lithium batteries. Energy Technol. 1, 77–84 (2013)
Wang, C., Zhang, Q., Wu, Q.H., Ng, T.W., Wong, T., Ren, J., Shi, Z., Lee, C.S., Lee, S.T., Zhang, W.: Facile synthesis of laminate-structured graphene sheet–Fe3O4 nanocomposites with superior high reversible specific capacity and cyclic stability for lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2, 10680–10688 (2012)
Wu, Q.H., Wang, C., Ren, J.G.: Sn and SnO2-graphene composites as anode materials for lithium ion batteries. Ionics 19, 1875–1882 (2013)
Ke, F.S., Huang, L., Jamison, L., Xue, L.J., Wei, G.Z., Li, J.T., Zhou, X.D., Sun, S.G.: Nanoscale tin-based intermetallic electrodes encapsulated in microporous copper substrate as the negative electrode with a high rate capacity and a long cycleability for lithium-ion batteries. Nano Energy 2, 595–603 (2013)
Atar, N., Eren, T., Lütfi Yola, M., Karimi-Maleh, H., Demirdögen, B.: Magnetic iron oxide and iron oxide@gold nanoparticles anchored nitrogen and sulfur-functionalized reduced graphene oxide electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation. RSC Adv. 5, 26402–26409 (2015)
Hua, R., Li, Z h: Sulfhydryl functionalized hydrogel with magnetism: synthesis, characterization, and adsorption behavior study for heavy metal removal. Chem. Eng. J. 249, 189–200 (2014)
Wang, Y., Li, Z.H., Hu, D.H., Lin, C.T., Li, J.H., Lin, Y.H.: Aptamer/graphene oxide nanocomplex for in situ molecular probing in living cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 9274–9276 (2010)
Lin, L., Liu, Y., Zhao, X., Li, J.H.: Sensitive and rapid screening of T4 polynucleotide kinase activity and inhibition based on coupled exonuclease reaction and graphene oxide platform. Anal. Chem. 83, 8396–8402 (2011)
Tang, L.H., Wang, Y., Li, Y.M., Feng, H.B., Lu, J., Li, J.H.: Preparation, structure, and electrochemical properties of reduced graphene sheet films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 2782–2789 (2009)
Wang, Y., Shao, Y.Y., Matson, D.W., Li, J.H., Lin, Y.H.: Nitrogen-doped graphene in electrochemical biosensing. ACS Nano 4, 1790–1798 (2010)
Wang, Z.H., Xia, J.F., Zhu, L.Y., Chen, X.Y., Zhang, F.F., Yao, S.Y., Li, Y.H., Xia, Y.Z.: A selective voltammetric method for detecting dopamine at quercetin modified electrode incorporating graphene. Electroanalysis 23, 2463–2471 (2012)
Wang, Z.H., Xia, J.F., Zhu, L.Y., Zhang, F.F., Guo, X.M., Li, Y.H., Xia, Y.Z.: The fabrication of poly (acridine orange)/graphene modified electrode with electrolysis micelle disruption method for selective determination of uric acid. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 161, 131–136 (2012)
Wang, X.L., Bai, H., Yao, Z.Y., Liu, A.R., Shi, G.Q.: Electrically conductive and mechanically strong biomimetic chitosan/reduced graphene oxide composite films. J. Mater. Chem. 20, 9032–9036 (2010)
Wang, X.L., Bai, H., Jia, Y.Y., Zhi, L.J., Qu, L.T., Xu, Y.X., Li, C., Shi, G.Q.: Synthesis of CaCO3/graphene composite crystals for ultra-strong structural materials. RSC Adv. 2, 2154–2160 (2012)
Pradhan, P., Giri, J., Rieken, F., Koch, C., Mykhaylyk, O., Doblinger, M., Banerjee, R., Bahadur, D., Plank, C.: Targeted temperature sensitive magnetic liposomes for thermo-chemotherapy. J. Control. Release 142, 108–121 (2010)
Okushima, S., Nisisako, T., Torii, T., Higuchi, T.: Controlled production of monodisperse double emulsions by two-step droplet break-up in microfluidic devices. Langmuir 20, 9905–9908 (2004)
Ma, E.L., Li, J.J., Zhao, N.Q., Liu, E.Z., He, C.N., Shi, C.S.: Preparation of reduced graphene oxide/Fe3O4 nanocomposite and its microwave electromagnetic properties. Mater. Lett. 91, 209–212 (2013)
Zhou, C.J., Zhou, W.J., Zhang, H.X., Wang, H.Y., Li, J., Zhou, S.H., Wang, J.Y., Liu, J., Luo, B.S., Zou, J.D.: Preparation of Fe3O4-embedded graphene oxide for removal of methylene blue. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39, 6679–6685 (2014)
Jing, L.Y., Fu, A.P., Li, H.L., Liu, J.Q., Guo, P.Z., Wang, Y.Q., Zhao, X.S.: One-step solvothermal preparation of Fe3O4/graphene composites at elevated temperature and their application as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 4, 59981–59989 (2014)
Buyukozturk, F., Benneyan, J.C., Carrier, R.L.: Impact of emulsion-based drug delivery systems on intestinal permeability and drug release kinetics. J. Control. Release 142, 22–30 (2010)
Gai, S.L., Yang, P.P., Li, C.X., Wang, W.X., Dai, Y.L., Niu, N., Lin, J.: Synthesis of magnetic, up-conversion luminescent, and mesoporous core–shell-structured nanocomposites as drug carriers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 20, 1166–1172 (2010)
Wu, Y., Fei, Z.Z., Lee, L.J., Wyslouzil, B.E.: Coaxial electrohydrodynamic spraying of plasmid DNA/polyethylenimine (PEI) polyplexes for enhanced nonviral gene delivery. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 105, 834–842 (2010)
Gupta, A.K., Wells, S.: Surface-modified superparamagnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery: preparation, characterization, and cytotoxicity studies. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 3, 66–73 (2004)
Kim, D.K., Zhang, Y., Voit, W., Rao, K.V., Muhammed, M.: Synthesis and characterization of surfactant-coated superparamagnetic monodispersed iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 225, 30–36 (2001)
Hummers, W.S., Offeman, R.E.: Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80, 1339–1339 (1958)
Honda, M., Baba, Y., Shimoyama, I., Sekiguchi, T.: A fluorescence XAFS measurement instrument in the soft x-ray region toward observation under operando conditions. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 86, 035103 (2015)
Bagbi, Y., Sarswat, A., Mohan, D., Pandey, A., Solanki, P.R.: Lead and chromium adsorption from water using L-cysteine functionalized magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–15 (2015)
Xiao, J., Lv, W., Xie, Z., Tan, Y., Song, Y., Zheng, Q.: Environmentally friendly reduced graphene oxide as a broad-spectrum adsorbent for anionic and cationic dyes via π–π interactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 12126 (2016)
Chen, Y., Song, B., Tang, X., Lu, L., Xue, J.: One-step synthesis of hollow porous Fe3O4 beads—reduced graphene oxide composites with superior battery performance. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 17656–17662 (2012)
Honda, M., Baba, Y., Shimoyama, I., Sekiguchi, T.: A fluorescence XAFS measurement instrument in the soft x-ray region toward observation under operando conditions. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 86, 035103–5 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahebalzamani, H., Mehrani, K., Hosseini, H.R.M. et al. Effect of Cysteine Substitutions on the Structural and Magnetic Properties of Fe3O4–Cysteine/RGO and Fe3O4/RGO–Cysteine Nanocomposites. J Supercond Nov Magn 32, 1299–1306 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4779-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4779-4